Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- What Are Ceramic Capacitors?
- Key Features of Ceramic Capacitors
- Types of Ceramic Capacitors
- Applications of Ceramic Capacitors
- Advantages of Ceramic Capacitors
- Choosing the Right Ceramic Capacitor
- Ceramic Capacitors vs. Other Capacitors
- Conclusion
Introduction:
Ceramic capacitors are indispensible in modern electronics. They perform various roles in circuits that vary from smart-phones to industrial equipment. They offer reliable performance, cost effectiveness, and the flexibility involved in selecting a suitable type for your project. Here’s what you need to know about the structure, applications, and types of ceramic capacitors.
What are Ceramic Capacitors?
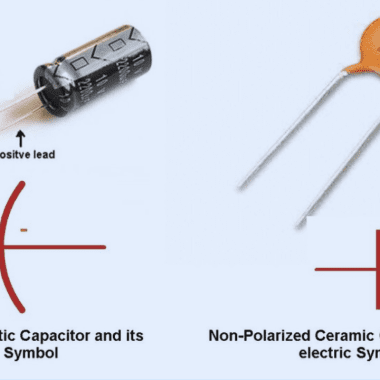
A ceramic capacitor is a type of passive electronic component that utilizes a ceramic material as the dielectric. They are used to store and release electrical energy, often as energy buffers or filters or coupling elements in a circuit. Their name derives from the ceramic dielectric that separates conductive plates in the capacitor.
The widespread use of ceramic capacitors is attributed to stability, inexpensiveness, and availability over an extremely wide range of values. There is no polarity in them, unlike those electrolytic capacitors, which limits its usage in both AC and DC circuits. Such flexibility and reliability make ceramic capacitors a first choice for engineers involved in consumer electronics, telecommunications, and industrial control systems.
Key Features of Ceramic Capacitors
- Highly Easy to Use: The ceramic capacitors connect in almost all directions, making them very
- simple to use in AC circuits.
- High Stability: They work over a wide temperature and frequency range providing strong stability even in extreme conditions
- Compact size: Ceramic capacitors come with small form factors available, they are therefore suitable for compact devices like smartphones and tablets for wearables.
- Huge Capacitance Range: Ceramic capacitors can have a huge range of values from picofarads (pF) to microfarads (μF).
Classes of Ceramic Capacitors
Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCC):

MLCCs consist of numerous layers of ceramic and metal electrodes that alternate in the process of increasing the capacitance while still making it not too large.
Common Application: MLCCs are heavily used in many consumer electronics products, from phones to computers, because of their excellent performance in high-frequency circuits.
Ceramic Disc Capacitors:

- These capacitors utilize disc-shaped ceramic dielectric and primarily used in high-voltage circuits.
- Typical Applications: Disc capacitors are used in power supplies, televisions, and RF.
Applications of Ceramic Capacitors:

The ceramic capacitors are multi-purpose which allows them to be used in a variety of electronic systems. The applications mostly include the following:
1.Noise Suppression: The ceramic capacitors suppress unwanted noises and very high frequency signals existent within the power lines to allow the electrical components work properly.
2.Bypass Capacitors : Ceramic capacitors are used as bypass capacitors in digital circuits that ensure that voltage supply gets stabilized as the fluctuations decrease.
3.Timing Circuits : Ceramic capacitors are used in oscillators and timing circuits for controlling the electronic signals as their timing.
4. Power Management : When the whole system is involved, power supply circuits help to cut out voltage spikes through the help of ceramic capacitors and make the whole system more stable.
Advantages of Ceramic Capacitors:
- Cheap: This is the cheapest type of capacitors, allowing for mass production and usage in consumer electronics.
- Reliability: It withstands changes in temperature and voltage very well, with zero or minimum leakage or variation.
- Lower ESR: Lower ESR means wasting more energy in heat form and increases the overall efficiency of the circuit.
Choosing the Correct Ceramic Capacitor
To select the right ceramic capacitor for your project, you must be aware of some easy factors:
- They must be chosen in the right capacitance for the specific application, whether it’s filtering, coupling, or decoupling signals.
- The voltage rating for the capacitor should always be greater than the greatest voltage in your circuit to avoid breakdowns.
- For circuits used in variable temperature environments, capacitors with a stable temperature coefficient should be used.
- Packaging Size: Consider the physical size and shape of the capacitor so that it will fit inside the space provisioned for your project, especially for PCB designs.
Ceramic Capacitors vs. Other Capacitors:
Compare the ceramic type with others, for example with electrolytic or tantalum capacitors. Ceramic capacitors are non-polarised, and in appearance, they look much better in high-frequency applications than electrolytic capacitors. Tantalum capacitors are even stable, but they cost much more than ceramic capacitors, so, as a rule, for most general-purpose application ceramic capacitors are preferable.
Conclusion
Ceramic capacitors have become an indispensable part of many different types of electronics. They offer solid guarantees in terms of reliability, cost effectiveness, and application. Based on your requirement, be it a smartphone or a power supply for a desktop computer, you can achieve stable operation in various control systems through ceramic capacitors. When you know their type and application, you can choose the appropriate ceramic capacitor while working on an electronics project in order to guarantee efficient and reliable operation.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.