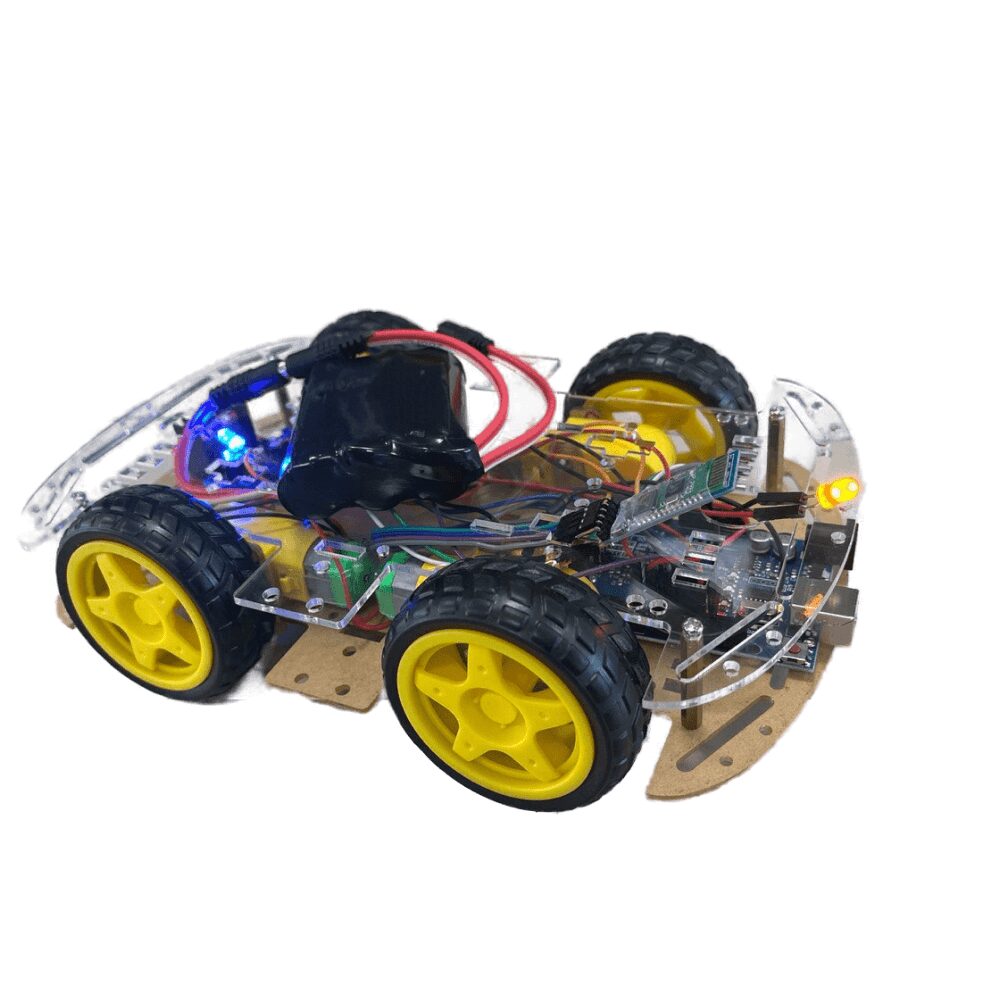
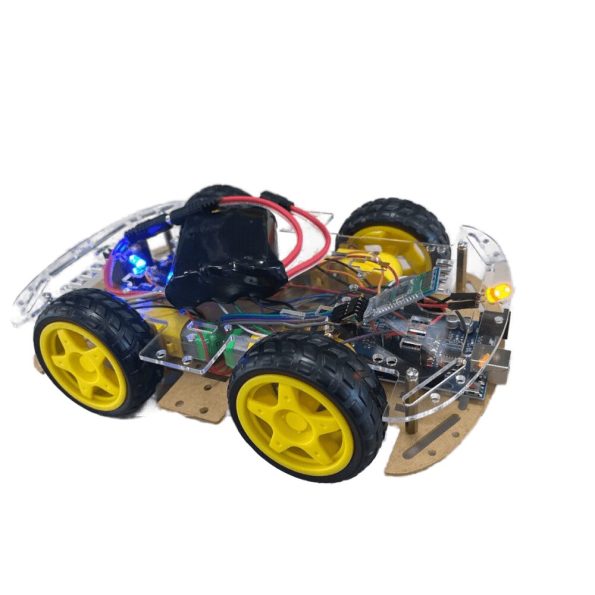
Arduino ide should be read since if you are interested in robotics technology or if you just want to create an easily controlled robot, this article is for you. This is an in-depth tutorial that helps you build a robot vehicle capable of receiving commands over Bluetooth and interacting with a custom Android application.
Step 1: Making the Body of the Robot
The body is the robot’s structural strength upon which all the electrical components sit. To make a lightweight and rigid structure:
Sunboards have the same strength as cardboards and are less expensive.
Using a craft knife or laser cutter, cut out the following pieces:
2 rectangular pieces of 10.5 x 13.5 cm which will serve as the base and top plates.
2 strips of 7.5 x 2.3 cm which can act as side supports.
2 strips of 11.5 x 2.3 cm serving as front and rear supports.
1 strip of 4.3 x 2.3 cms which can be used for the battery compartment.
2 strips of 10.5 x 3.5 cm for the motor mounts.
You can now glue, screw, or hot glue the components together to complete the chassis.
It is worth cutting extra pieces for easy replacement while working through construction.
Step 2: Configuring the Motors
In pairs, from the left, right and across each pair of the motors connect all the four motors in parallel
Connect pins in cross wiring to allow for the connection.
This section may also be supported by the video or circuit schematic.
Step 3: Motors Connections to the Motor Driver
With L298N Module:
Insert motors onto the screw terminal of the driver.
The polarity of controls and direction sequence is determined by the inputs to the Arduino.
Step 4: Connection of the Motor Driver to the Arduino ide
Design how the motor driver is to be attached on the Arduino Uno board:
Proper connection of female bergstrips, male bergstrips and relimate connectors.
Use an Arduino Protoshield.Try the removed connection sockets.
Step 5: Introducing of RGB Neopixel LEDs
Decorate your robot making it look more cool and attractive using RGB Neopixel LEDs
Fix the LEDs on the Arduino Board.
Modify the colors of the LEDs in the Android app developed for this purpose.
Step 6: Designing the Custom Android App for the User
With the help of MIT App Inventor:
The Bluetooth capability must be integrated while constructing the interfaces so commands can be sent.
Moving the robot, directing LEDs and coloring it, and creating patterns with them.
Step 7: Circuit Diagram as well as Assembly
See below the complete circuit diagram:
Check that every connection is predetermined in construction is persistent and secure.
Make sure to confirm the connectivity between the motor driver, Arduino, and Bluetooth once again.
Step 8: Tuning and Adjustment
Perform some movement tests for the robot and check the LED in the robot as well.
Realign the motors and the Android application accordingly.
Components Required:
An Arduino Uno.
An L298N Motor Driver.
4 DC motors.
Solar boards.
RGB Neon pixcels LED
We need a bluetooth module for arduino.
An android phone.
The software MIT App Inventor.
Jumping wires.
Bergstrips.
Relimate connectors.
Tips and Variations:
Precision can be improved by switching to a more complex motor driver.
Integrate any sensors for line following or for obstacle avoidance.
Try other types of Arduino boards or microcontrollers.
Using the above procedures, you have built a fully operational Bluetooth controlled wireless robot car which is AKB01 all by yourself and have improved your robotics skills and knowledge.
Bluetooth Controlled Robot Arduino Code
The code for Bluetooth controlled robot which basis is Arduino is somehow complicated. This reason made us break the total code then into three sections.
The working of this circuit is very simple and easy to understand. First, we have the Arduino which is working as the brains of the circuit. Next, we have the Bluetooth module. The Bluetooth module is connected to pin 13 and 10 of the Arduino that we are using as the software serial. Next, we are using pins 11,12,8, and 7 to connect our WS2812B RGB leds. Finally, we are using pins 9, 6, 5 and 4 to connect the L298N motor driver IC that is driving four of our motors. Finally, to power it all up, we are using a 9V battery.
Arduino | L298N |
3 | IN1 |
9 | IN2 |
5 | IN3 |
6 | IN4 |
VIN | +5V |
GND | GND |
Arduino | HC05 |
10 | Tx |
11 | Rx |
+5V | VCC |
GND | GND |
Arduino | NeoPixel |
8 | Left LED |
7 | Right LED |
12 | Front LED Data |
13 | Back LED Data |